
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography
- Hwi Seung Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, In Young Bae, Woo Je Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):104-117. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0081
- 3,238 View
- 176 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
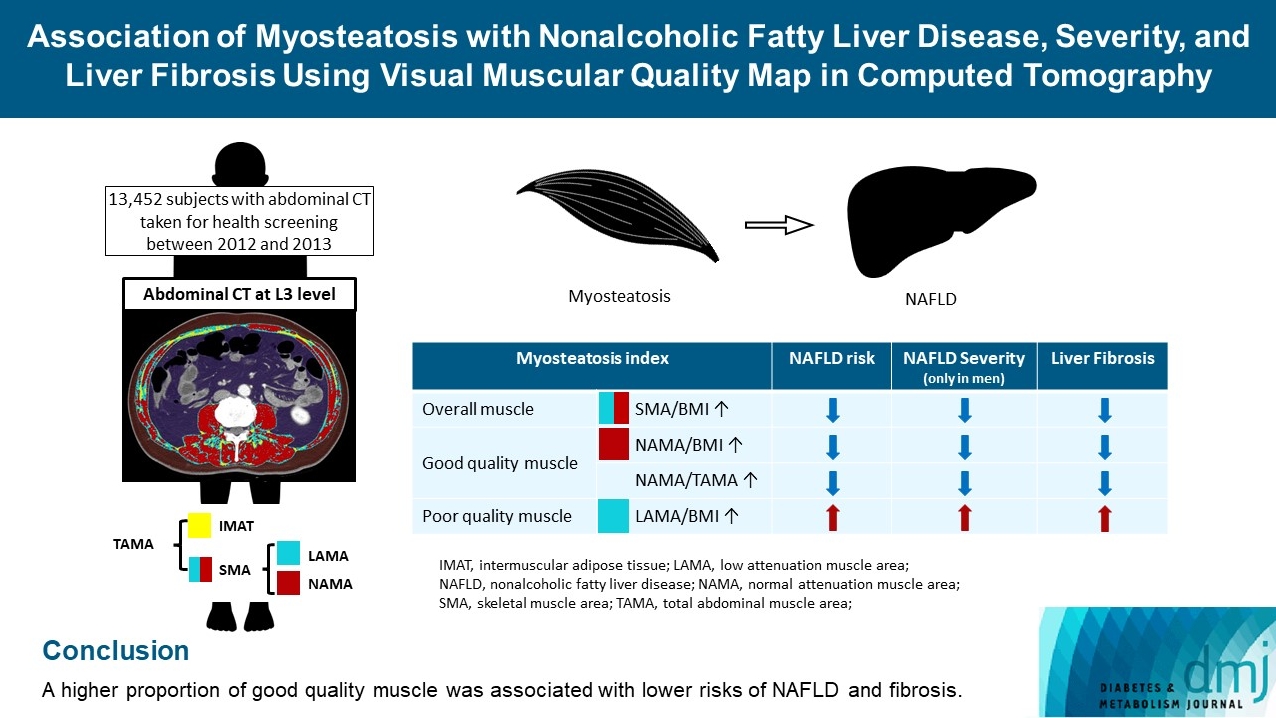
ePub - Background
The association of myosteatosis measured using visual muscular quality map in computed tomography (CT) with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), its severity, and fibrosis was analyzed in a large population.
Methods
Subjects (n=13,452) with abdominal CT between 2012 and 2013 were measured total abdominal muscle area (TAMA) at L3 level. TAMA was segmented into intramuscular adipose tissue and skeletal muscle area (SMA), which was further classified into normal attenuation muscle area (NAMA) and low attenuation muscle area (LAMA). The following variables were adopted as indicators of myosteatosis: SMA/body mass index (BMI), NAMA/BMI, NAMA/TAMA, and LAMA/BMI. NAFLD and its severity were assessed by ultrasonography, and liver fibrosis was measured by calculating the NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) and fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4) scores.
Results
According to multiple logistic regression analyses, as quartiles of SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA increased, the odds ratios (ORs) for NAFLD decreased in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all). The ORs of moderate/severe NAFLD were significantly higher in the Q1 group than in the Q4 group for SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA in men. The ORs of intermediate/high liver fibrosis scores assessed by NFS and FIB-4 scores increased linearly with decreasing quartiles for SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all). Conversely, the risk for NAFLD and fibrosis were positively associated with LAMA/BMI quartiles in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all).
Conclusion
A higher proportion of good quality muscle was associated with lower risks of NAFLD and fibrosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
Hwi Seung Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 304. CrossRef - Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 301. CrossRef - Sarcopenia, a condition shared by various diseases: can we alleviate or delay the progression?
Giovanni Tarantino, Gaia Sinatti, Vincenzo Citro, Silvano Santini, Clara Balsano
Internal and Emergency Medicine.2023; 18(7): 1887. CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Current view of the surgical anatomy of the anterolateral abdominal wall muscles and their aponeuroses
A.V. Pavlov, A.S. Baranova, A.V. Fedoseyev, A.I. Vvedensky, G.S. Lazutina, N.V. Ovchinnikova, I.V. Bakharev
Operativnaya khirurgiya i klinicheskaya anatomiya (Pirogovskii nauchnyi zhurnal).2023; 7(3): 44. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Adults
W. Guo, X. Zhao, D. Cheng, X. Liang, M. Miao, X. Li, J. Lu, N. Xu, Shuang Hu, Qun Zhang
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(11): 960. CrossRef
- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
- Drug/Regimen
- Dulaglutide as an Effective Replacement for Prandial Insulin in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Review
- Hwi Seung Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):948-953. Published online February 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0180

- 5,760 View
- 232 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Dulaglutide, a weekly injectable glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, has demonstrated effectiveness when combined with basal insulin. We examined whether the efficacy of dulaglutide is comparable to that of prandial insulin in kidney transplant (KT) recipients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) undergoing multiple daily insulin injection (MDI) therapy. Thirty-seven patients, who switched from MDI therapy to basal insulin and dulaglutide, were retrospectively analyzed. Changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, body weight, and basal insulin dose were evaluated over 6 months. Dulaglutide was comparable to three injections of prandial insulin in terms of glycemic control (HbA1c 7.1% vs. 7.0%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.53 to 0.28; P=0.53). The basal insulin and dulaglutide combination resulted in a reduction in FPG levels by 9.7 mg/dL (95% CI, 2.09 to 41.54; P=0.03), in body weight by 4.9 kg (95% CI, 2.87 to 6.98; P<0.001), and in basal insulin dose by 9.52 IU (95% CI, 5.80 to 3.23; P<0.001). Once-weekly dulaglutide may be an effective alternative for thrice-daily prandial insulin in KT recipients with T2DM currently receiving MDI therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetic Kidney Disease in Post-Kidney Transplant Patients
Ngoc-Yen T. Pham, Diego Cruz, Luis Madera-Marin, Raja Ravender, Pablo Garcia
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(3): 793. CrossRef - Safety and efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pajaree Krisanapan, Supawadee Suppadungsuk, Kanokporn Sanpawithayakul, Charat Thongprayoon, Pattharawin Pattharanitima, Supawit Tangpanithandee, Michael A Mao, Jing Miao, Wisit Cheungpasitporn
Clinical Kidney Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sweet and simple as syrup: A review and guidance for use of novel antihyperglycemic agents for post‐transplant diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation
S. Elise Lawrence, Mary Moss Chandran, Jeong M. Park, Helen Sweiss, Thomas Jensen, Palak Choksi, Barrett Crowther
Clinical Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Drugs for the Management of Diabetes Kidney Transplant Patients: A Literature Review
Nancy Daniela Valencia-Morales, Beatriz Rodríguez-Cubillo, Rómulo Katsu Loayza-López, Maria Ángeles Moreno de la Higuera, Ana Isabel Sánchez-Fructuoso
Life.2023; 13(6): 1265. CrossRef - Uso de los agonistas del receptor del péptido similar al glucagón tipo 1 en pacientes trasplantados renales
Luis Alberto Vigara, Florentino Villanego, Cristhian Orellana, Myriam Eady, María Gabriela Sánchez, Marta Alonso, María Belén García, José Manuel Amaro, Teresa García, Auxiliadora Mazuecos
Nefrología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tolerability and Effectiveness of Switching to Dulaglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled With Insulin Therapy
Youngsook Kim, Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diabetic Kidney Disease in Post-Kidney Transplant Patients
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
-
- Asian Subpopulations May Exhibit Greater Cardiovascular Benefit from Long-Acting Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists: A Meta-Analysis of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials
- Yu Mi Kang, Yun Kyung Cho, Jiwoo Lee, Seung Eun Lee, Woo Je Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Ye-Jee Kim, Chang Hee Jung, Michael A. Nauck
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):410-421. Published online December 27, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0070
- 6,321 View
- 137 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Based on reported results of three large cardiovascular outcome trials (CVOTs) of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), we aimed to investigate the overall effect of GLP-1 RAs on major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) and to identify subpopulations exhibiting the greatest cardiovascular (CV) benefit.
Methods Three CVOTs reporting effects of long-acting GLP-1 RAs were included: LEADER (liraglutide), SUSTAIN-6 (semaglutide), and EXSCEL (exenatide once weekly). In all studies, the primary endpoint was three-point MACE, comprising CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal stroke. Overall effect estimates were calculated as hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using the random-effects model; subgroup analyses reported in the original studies were similarly analyzed.
Results Overall, statistically significant risk reductions in MACE and CV death were observed. Subgroup analysis indicated a significant racial difference with respect to CV benefit (
P for interaction <0.001), and more substantial risk reductions were observed in subjects of African origin (relative risk [RR], 0.78; 95% CI, 0.60 to 0.99) and in Asians (RR, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.09 to 1.32). However,post hoc analysis (Bonferroni method) revealed that only Asians exhibited a significantly greater CV benefit from treatment, compared with white subjects (P <0.0001).Conclusion Long-acting GLP-1 RAs reduced risks of MACE and CV deaths in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Our findings of a particularly effective reduction in CV events with GLP-1 RA in Asian populations merits further exploration and dedicated trials in specific populations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sex, racial, ethnic, and geographical disparities in major adverse cardiovascular outcome of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among patients with and without diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized controlled trials,
Frederick Berro Rivera, Nathan Ross B. Bantayan, John Paul Aparece, Linnaeus Louisse A. Cruz, John Vincent Magallong, Polyn Luz Pine, Anne Mira Nicca Idian-Javier, Grace Nooriza O. Lumbang, Edgar V. Lerma, Kyla M. Lara-Breitinger, Martha Gulati, Krishnasw
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronary Artery Disease in South Asian Patients: Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Pathogenesis and Treatments
Vincenzo Sucato, Giuseppe Coppola, Girolamo Manno, Giuseppe Vadalà, Giuseppina Novo, Egle Corrado, Alfredo Ruggero Galassi
Current Problems in Cardiology.2023; 48(8): 101228. CrossRef - Retrospective Analysis of the Effectiveness of Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Cardiometabolic Parameters in Japanese Clinical Settings
Hodaka Yamada, Masashi Yoshida, Shunsuke Funazaki, Jun Morimoto, Shiori Tonezawa, Asuka Takahashi, Shuichi Nagashima, Kimura Masahiko, Otsuka Kiyoshi, Kazuo Hara
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2023; 10(4): 176. CrossRef - Efficacy of treatment with glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists-1 in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
L. Yu. Khamnueva, L. S. Andreeva
Problems of Endocrinology.2023; 69(2): 38. CrossRef - Role of diabetes in stroke: Recent advances in pathophysiology and clinical management
Sian A. Bradley, Kevin J. Spring, Roy G. Beran, Dimitrios Chatzis, Murray C. Killingsworth, Sonu M. M. Bhaskar
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity Pillars Roundtable: Obesity and East Asians
Harold Edward Bays, Jennifer Ng, Jeffrey Sicat, Michelle Look
Obesity Pillars.2022; 2: 100011. CrossRef - Pathophysiology, phenotypes and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Indian and Chinese populations
Calvin Ke, K. M. Venkat Narayan, Juliana C. N. Chan, Prabhat Jha, Baiju R. Shah
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(7): 413. CrossRef - Effect of race on cardiometabolic responses to once-weekly exenatide: insights from the Exenatide Study of Cardiovascular Event Lowering (EXSCEL)
Timothy M. E. Davis, Anna Giczewska, Yuliya Lokhnygina, Robert J. Mentz, Naveed Sattar, Rury R. Holman
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Generalizability of the Results of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Xiaoling Cai, Linong Ji
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(7): 1861. CrossRef - Current trends in epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk management in type 2 diabetes
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Metabolism.2021; 123: 154838. CrossRef - Sex and ethnic differences in the cardiovascular complications of type 2 diabetes
Jian L. Yeo, Emer M. Brady, Gerry P. McCann, Gaurav S. Gulsin
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882110342. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yuan Zhu, Jiao Xu, Dong Zhang, Xingyu Mu, Yi Shi, Shangtao Chen, Zengxiang Wu, Shuangqing Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in type 2 diabetes patients in endocrinology clinics of Islamabad, Pakistan
Matiullah Kamin, SajjadAli Khan, UmarYousaf Raja, Osama Ishtiaq, Asmara Malik, Tejhmal Rehman, MuhammadUmar Wahab
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(5): 456. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in South Asians: a Unique Population with a Growing Challenge
Afreen I. Shariff, Nitya Kumar, William S. Yancy, Leonor Corsino
Current Diabetes Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Antihypertensive and Renal Mechanisms of SGLT2 (Sodium-Glucose Linked Transporter 2) Inhibitors
Christopher S. Wilcox
Hypertension.2020; 75(4): 894. CrossRef - Subpopulation Differences in the Cardiovascular Efficacy of Long-Acting Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Liyun He, Na Yang, Lingling Xu, Fan Ping, Wei Li, Yuxiu Li, Huabing Zhang
Diabetes Therapy.2020; 11(9): 2121. CrossRef - 2020 Consensus of Taiwan Society of Cardiology on the pharmacological management of patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases
Chern-En Chiang, Kwo-Chang Ueng, Ting-Hsing Chao, Tsung-Hsien Lin, Yih-Jer Wu, Kang-Ling Wang, Shih-Hsien Sung, Hung-I Yeh, Yi-Heng Li, Ping-Yen Liu, Kuan-Cheng Chang, Kou-Gi Shyu, Jin-Long Huang, Cheng-Dao Tsai, Huei-Fong Hung, Ming-En Liu, Tze-Fan Chao,
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2020; 83(7): 587. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef
- Sex, racial, ethnic, and geographical disparities in major adverse cardiovascular outcome of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among patients with and without diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized controlled trials,

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





